Understanding Aqueous Cleaners Are A Part Of Cleaning Agents
Introduction to Aqueous Cleaners
Aqueous cleaners are super important for cleaning stuff, especially when it comes to cleaning different parts. These cleaners are usually made of water mixed with detergents, surfactants (which help to clean), and special chemicals. They’re made this way to make sure they can really get rid of all sorts of dirt and grime, like dirt, grease, and oil, from all kinds of parts, whether they’re made of metal or plastic.
Explore Mount Carmel Wyoming Shutting Down

Benefits of Aqueous Cleaners
- Safety: Aqueous cleaners offer enhanced safety compared to solvent-based cleaners. They are typically non-flammable and have lower toxicity levels, ensuring a safer working environment for operators.
- Environmental Friendliness: One of the significant advantages of aqueous cleaners is their minimal environmental impact. They produce fewer emissions and are more biodegradable than solvent-based counterparts, aligning with sustainable practices.
- Versatility: Aqueous cleaners demonstrate versatility by effectively removing contaminants from various surfaces. These cleaners can tackle diverse cleaning needs across industries, whether dirt, grease, oil, or rust.
- Ease of Use: These cleaners are designed to be user-friendly and adaptable to different cleaning methods, including spray, immersion, and ultrasonic cleaning. This versatility simplifies the cleaning process and enhances overall efficiency.
- Cost-effectiveness: Aqueous cleaners provide a cost-effective solution for parts cleaning operations. They offer efficient cleaning performance at a relatively lower cost than solvent-based alternatives, contributing to overall cost savings.
Types of Aqueous Cleaners
- Alkaline Cleaners: Alkaline cleaners utilize alkaline chemicals to effectively break down and emulsify grease and oil. They are commonly used for cleaning metal parts in various industries.
- Acidic Cleaners: Acidic cleaners contain acids that effectively remove dust and other inorganic contaminants from metal and plastic surfaces.
- Chelating Cleaners: These cleaners contain chelating agents that bind to metal ions, preventing them from redepositing on cleaned surfaces. They are often used for cleaning metal parts exposed to corrosive environments.
- Surfactant Cleaners: Surfactant cleaners contain surfactants that lower the surface tension of water, allowing it to penetrate and remove dirt and grease from surfaces more effectively. They are suitable for cleaning various parts, including metal, plastic, and glass.
Visit 5 Tips to Stay Fit and Healthy
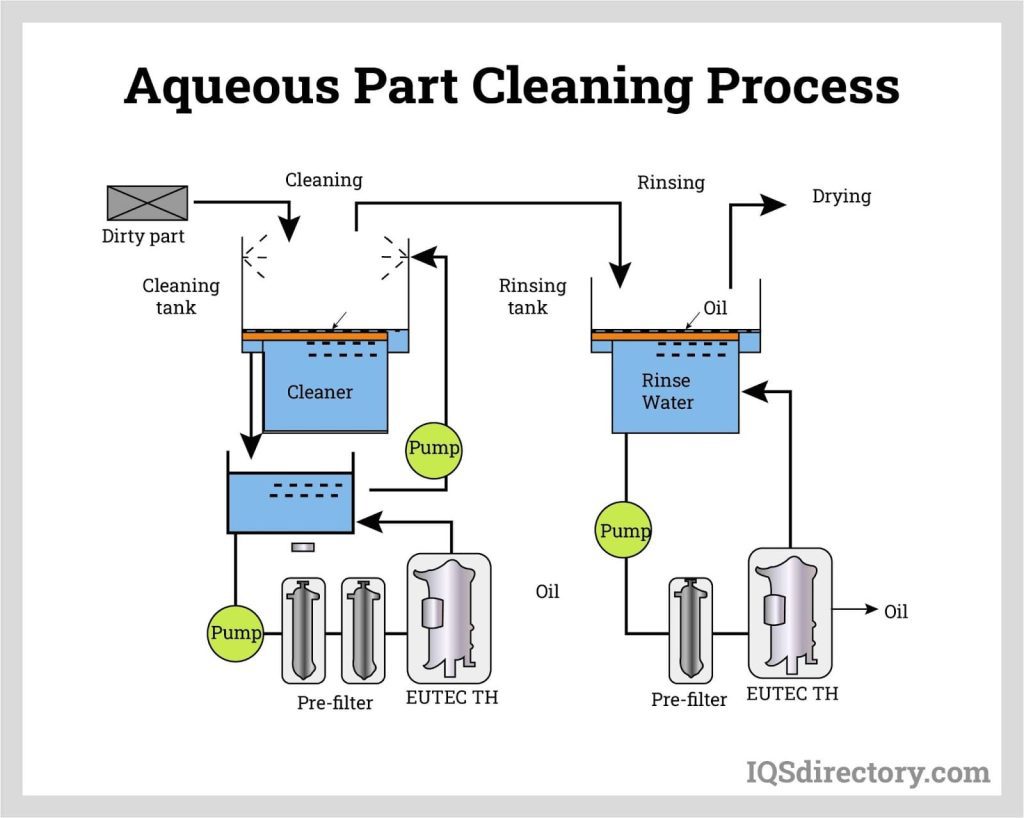
Household Uses of Aqueous Cleaners
Aqueous cleaners find numerous applications in household cleaning tasks:
- Floor Cleaning: They effectively remove dirt, grime, and spills from various types of flooring, including hardwood, tile, and laminate.
- Bathroom Cleaning: Aqueous cleaners are used to clean surfaces such as countertops, sinks, toilets, and bathtubs, removing soap scum, mildew, and hard water stains.
- Kitchen Cleaning: They are ideal for cleaning countertops, sinks, appliances, and cabinets, tackling grease, grime, and food spills effectively.
- Window and Mirror Cleaning: Aqueous cleaners ensure streak-free cleaning of windows and mirrors, removing dirt, grime, and streaks with ease.
- Upholstery Cleaning: They are used to clean upholstery on furniture, car seats, and pet beds, removing dirt, stains, and pet dander effectively.
Aqueous Cleaners in Electronics
Aqueous cleaners play a crucial role in electronic cleaning processes:
- Defluxing: In electronics manufacturing, refluxing involves removing flux residues from printed circuit boards (PCBs) after soldering processes. Aqueous cleaners effectively remove these residues without damaging the PCBs.
- PCB Cleaning: Aqueous cleaners clean PCBs before and after assembly to remove dust, dirt, and contaminants that may affect their performance.
- Component Cleaning: Electronic components such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors can also be cleaned using aqueous cleaners to ensure optimal functionality and longevity.
Understanding Aqueous Ammonia
Aqueous ammonia, also known as ammonium hydroxide, serves various applications across different industries:
- Cleaning: Aqueous ammonia is a strong cleaner that can effectively remove dirt, grease, and grime from surfaces such as glass, metal, and plastic.
- Agriculture: It is commonly used as a fertilizer to increase soil nitrogen content, promoting plant growth. It can also be used to control pests and diseases in agricultural settings.
- Manufacturing: Aqueous ammonia plays a vital role in the manufacturing process of various products, including plastics, textiles, and pharmaceuticals.
- Household Products: A common ingredient in household cleaning products such as window cleaners, degreasers, and drain cleaners, providing effective cleaning solutions for everyday tasks.

Safety Precautions for Handling Aqueous Ammonia
Due to its hazardous nature, proper safety precautions must be followed when handling aqueous ammonia:
- Protective Gear: Operators should wear appropriate protective gear, including gloves, goggles, and a respirator, to minimize exposure to the chemical.
- Ventilation: Work should be conducted in well-ventilated areas to prevent the buildup of ammonia vapors, which can be harmful when inhaled.
- Avoid Contact: Direct contact with aqueous ammonia should be avoided to prevent skin and eye irritation. Inhalation of vapors should also be avoided.
- Emergency Procedures: In case of accidental contact, affected areas should be immediately flushed with water, and medical attention should be sought if necessary.
Aqueous vs Solvent Cleaners
Aqueous and solvent cleaners differ in several aspects:
- Base: Aqueous cleaners use water as a base, while solvent cleaners use oil-based solvents.
- Cleaning Mechanism: Aqueous cleaners employ surfactants to emulsify and remove contaminants, whereas solvent cleaners dissolve dirt and grime using organic solvents.
- Safety: Aqueous cleaners are generally safer to use and handle than solvent cleaners, which can be hazardous and flammable.
- Environmental Impact: Aqueous cleaners have a lower environmental impact as they are more biodegradable and produce fewer harmful emissions than solvent cleaners.
- Applications: Aqueous cleaners are suitable for general cleaning and light-duty degreasing tasks, while solvent cleaners are preferred for heavy-duty degreasing and stubborn stain removal.

Comparison between aqueous and solvent cleaners:
Read 6 Ways to Help Your Loved One Break Free From Drug Addiction
| Comparison | Aqueous Cleaners | Solvent Cleaners |
|---|---|---|
| Base | Water | Oil |
| Cleaning Mechanism | Surfactants | Organic Solvents |
| Safety | Safe | Hazardous |
| Environmental Impact | Environmentally Friendly | Harmful to Environment |
| Applications | General Cleaning | Heavy-duty Cleaning |
Understanding Aqueous Solutions
Aqueous solutions, characterized by water serving as the solvent, are utilized across various fields:
- Chemical Reactions: Many chemical reactions occur in aqueous solutions, facilitating acid-base and precipitation reactions.
- Biological Processes: Many biological processes take place in aqueous environments, highlighting water’s crucial role in sustaining life.
- Medical Applications: Aqueous solutions are widely used in medical applications, including injectable medications, eye drops, and nasal sprays, for their compatibility with biological systems.

Aqueous Parts Washer Solutions
Aqueous parts washer solutions are specifically designed for practical parts cleaning:
- Components: These solutions typically contain water, detergents, emulsifiers, pH adjusters, corrosion inhibitors, and defoamers to facilitate thorough cleaning.
Benefits: Aqueous parts washer solutions offer efficient cleaning of dirt.






